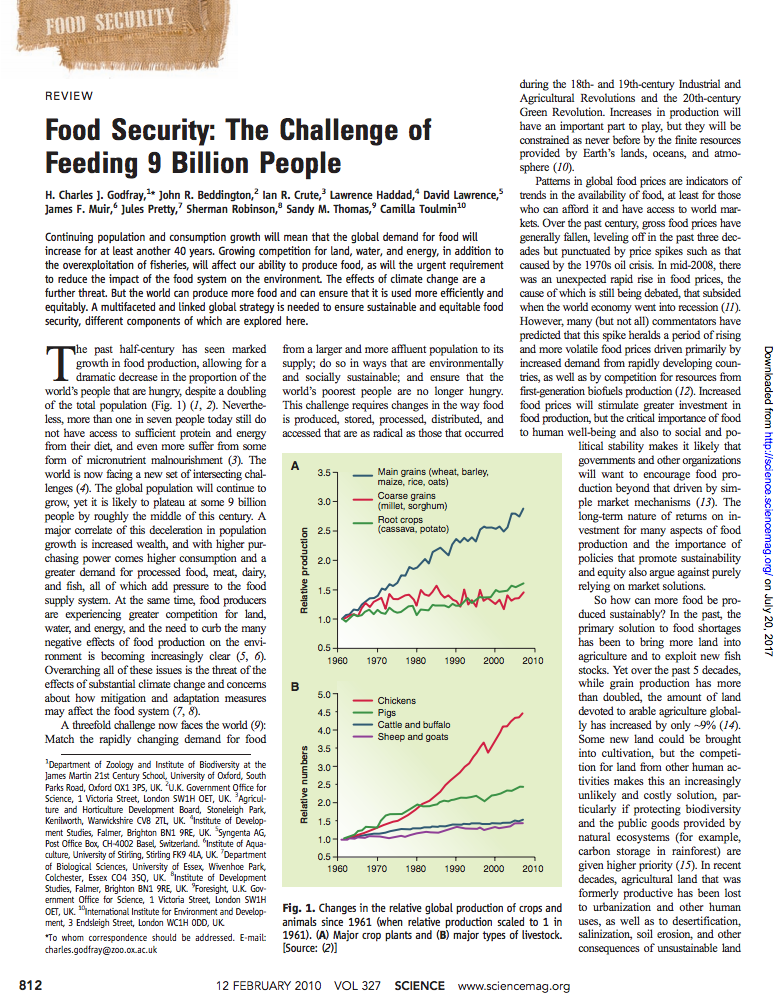
The Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Farmland Displacement in the Pearl River Delta, China
China is rapidly urbanizing and will inevitably face trade-offs between promoting economic growth through further urbanization and protecting fertile farmland against accelerated urban expansion. This paper presents how this dilemma is being addressed in one of the most rapidly urbanizing regions in China, the Pearl River Delta (PRD), by means of assessing urban growth and farmland dynamic, as well as their complex relationships.