Previsiones legales para el acceso a tierras de parte del campesinado y los indígenas - Luis Rojas BASE Investigaciones Sociales. (octubre 2013)
El presente material es un breve compendio de las leyes y normativas vigentes, que regulan el acceso a la tierra por parte de la población, con particular detalle en el caso de los campesinos y campesinas. En el caso de las comunidades indígenas, se hará una breve mención a la legislación correspondiente.
'Land grabbing' and international investment law: toward a global reconfiguration of property?
This yearbook chapter discusses the link between international investment law and commercial pressures on the world’s natural resources. It argues that changes in legal frameworks are redefining control over natural resources, and facilitating transitions toward more commercialised land relations. As pressures on resources increase, many national laws undermine the rights of people impacted by investments. If not properly thought through, international treaties to protect foreign investment could compound shortcomings of local and national governance.
Islamic Inheritance Laws and their impact on rural women. A synthesis of studies from Asia and West Africa and emerging recommendations
Analyses inheritance laws and their impacts on rural women in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Indonesia, Senegal, Togo and Mali. Focuses on Muslim societies, but also looks at how these differed from or influenced the inheritance practices of non-Muslim groups. Shows that women continue to be systematically denied their rights to inheritance, especially in rural areas.
Inclusive Land Governance in Mozambique: Good Law, Bad Politics?
Analyses inclusive land governance in Mozambique. Focuses on the country’s legal framework and the DUAT, the right to use and benefit from the land. The DUAT is a distinctive element of the Mozambican legislation that has land as the property of the state but recognises land use rights for occupants and users on the basis of a unitary system of tenure. The challenges of putting in practice what is thought to be one of Africa’s most progressive legal frameworks are discussed.
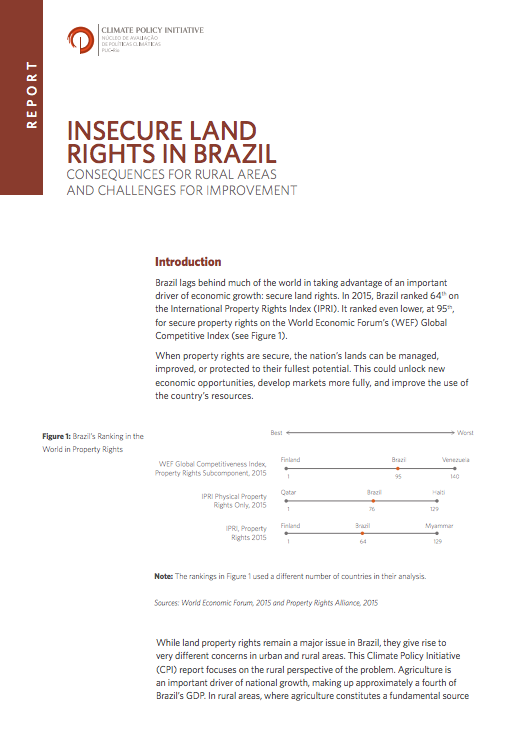
Insecure Land Rights in Brazil: Consequences for Rural Areas and Challenges for Improvement
Brazil lags behind much of the world in taking advantage of an important driver of economic growth: secure land rights. In 2015, Brazil ranked 64th on the International Property Rights Index (IPRI). It ranked even lower, at 95th, for secure property rights on the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Global Competitive Index.
When property rights are secure, the nation’s lands can be managed, improved, or protected to their fullest potential. This could unlock new economic opportunities, develop markets more fully, and improve the use of the country’s resources.
Property rights in a very poor country : tenure insecurity and investment in Ethiopia
This paper provides evidence from one of the poorest countries of the world that the property rights matter for efficiency, investment, and growth. With all land state-owned, the threat of land redistribution never appears far off the agenda. Land rental and leasing have been made legal, but transfer rights remain restricted and the perception of continuing tenure insecurity remains quite strong. Using a unique panel data set, this study investigates whether transfer rights and tenure insecurity affect household investment decisions, focusing on trees and shrubs.
Country Partnership Framework for the Lebanese Republic for the Period FY17-FY22
This Country Partnership Framework (CPF)
presents the World Bank Group (WBG) program and the
associated results framework for Lebanon for the period
FY17-FY22. In a fragile and conflict-prone environment, this
CPF aims at mitigating the immediate, and potentially
long-lasting impact of the Syria crisis on Lebanon, while
strengthening state institutions, addressing existing
vulnerabilities, and bolstering efforts on longer term
Country Partnership Framework for Sri Lanka for the Period FY17-FY20
The new Country Partnership Framework
(CPF or framework) presents the engagement of the World Bank
Group (WBG) in Sri Lanka over the next four years (fiscal
years 2017-20 (FY17–20)). The CPF aims to support the
achievement of some of the government’s medium-term goals in
areas that are critical for reducing extreme poverty and
promoting shared prosperity, and that are consistent with
the WBG’s comparative advantage. Notably, the CPF provides
Kingdom of Lesotho
Lesotho is one of the poorest countries
in Southern Africa, and has one of the highest income
inequality in the world. Home to about 2 million people,
Lesotho is surrounded by South Africa, the second largest
and most industrialized economy in Africa. Lesotho generates
income mainly by exporting textiles, water, and diamonds,
and is a member of the Southern African Customs Union
(SACU), the Southern African Development Community (SADC),
Country Partnership Framework for Uzbekistan for the Period FY16-FY20
This Country Partnership Framework (CPF)
covers the five-year period FY16-20. Anchored in the
government’s medium-term development plan as outlined in a
January 2015 Cabinet of Ministers Program of Action, it also
reflects the analysis and recommendations of the World Bank
Group’s (WBG) 2015 Systematic Country Diagnostic (SCD) for
Uzbekistan and the lessons learned from the Completion
Report of the previous CPS. The CPF’s objectives and
Country Partnership Framework for Bulgaria for the Period FY17-FY22
This program document presents the World
Bank Group (WBG) FY17-22 Country Partnership Framework (CPF)
for Bulgaria. The timing of the new CPF follows the
preparation of theSystematic Country Diagnostic (SCD)
prepared in FY15, and informs the areas and objectives ofthe
CPF in support of the WBG’s twin goals to reduce poverty and
boost shared prosperity1 for the bottom forty percent of the
population. The CPF proposes to focus WBG support in