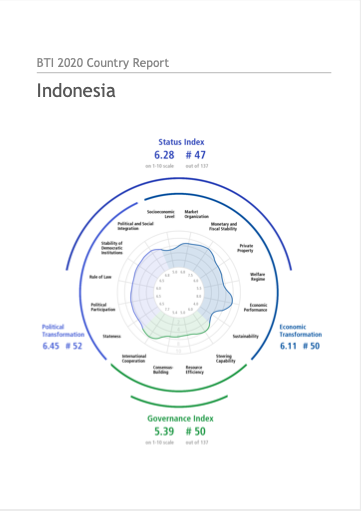
BTI 2020 Country Report Indonesia
Between 2017 and 2019, the quality of democracy in Indonesia continued to slowly but noticeably decline. While President Jokowi was able to de-escalate the conflict between the government and Islamist groups to some extent, he only managed to do so by integrating some Islamist themes and actors into the government structure. This, in turn, moved Indonesia ideologically and politically to the (religious) right. Religious, social and political minorities were the biggest losers of this shift.