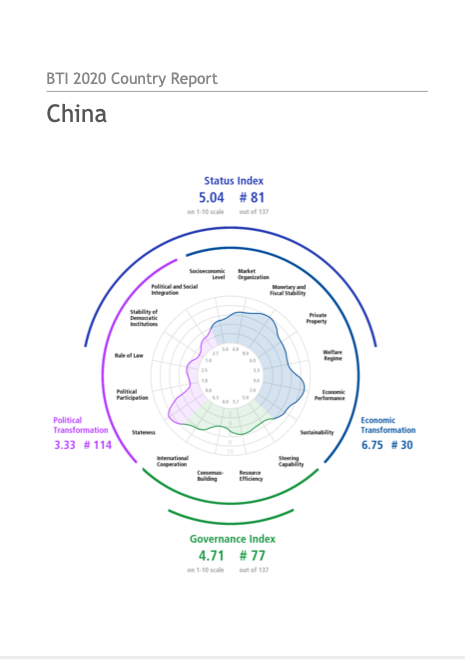
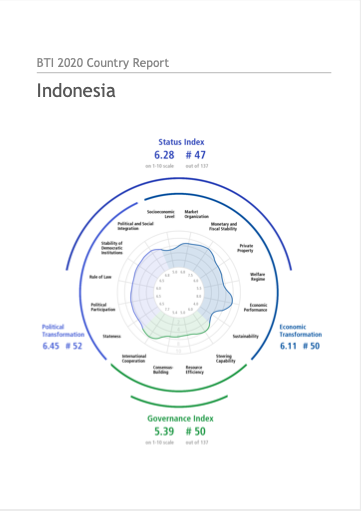
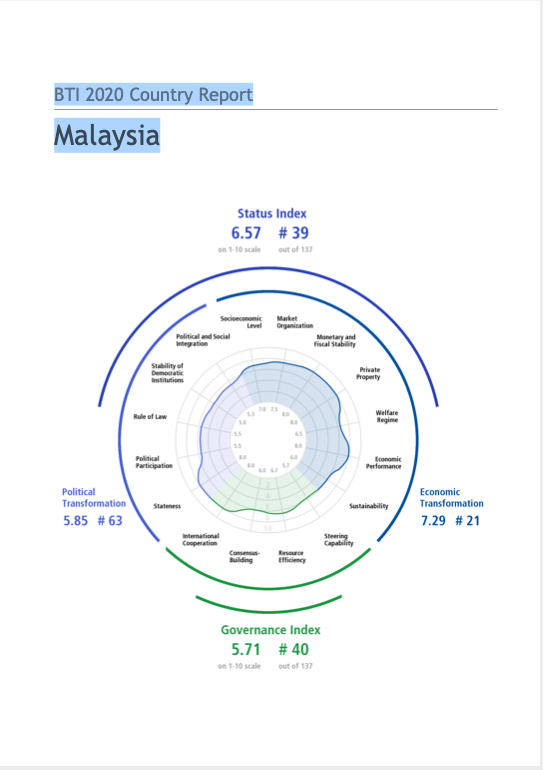
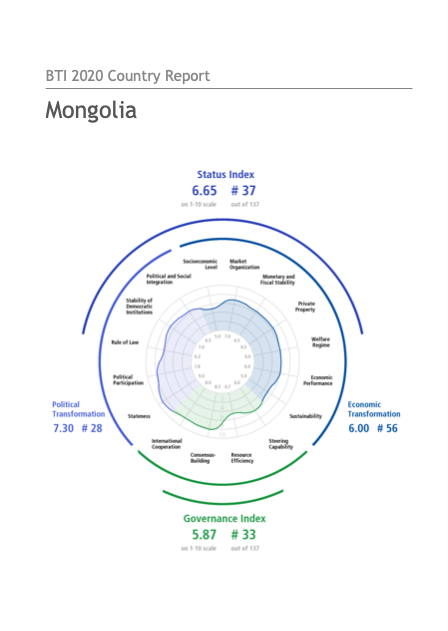
Money, power and the complexities of urban land corruption in Zimbabwe
ABSTRACT Urban land in Zimbabwe is a lucrative economic and thus political asset. Increased demand for urban land across the country has been driven by multiple factors including high rates of urbanization, increased rural-urban migration, urban population growth and serious challenges in housing provision post-independence. This paper uses desk research to map out the actors and contestations over land.