Location
NMBU's mission is to contribute to the well-being of the planet. Our interdisciplinary research generates innovations in food, health, environmental protection, climate and sustainable use of natural resources.
About NMBU
NMBU's research is enabling people all over the world to tackle the big, global challenges regarding the environment, sustainable development, how to improve human and animal health, renewable energy sources, food production, and land- and resource management.
Members:
Resources
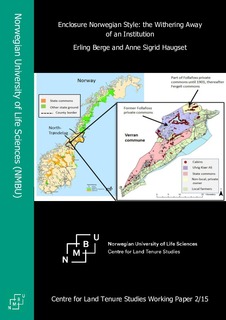
Displaying 41 - 45 of 98Enclosure Norwegian style : the withering away of an institution
More than 200 years after the King sold one of the “King’s commons” of Follafoss (located inthe current Verran municipality) to urban timber merchants, local people in some ways still behave as if the area is a kind of commons. The paper will outline the history of the transformation of the area from an 18th century King’s commons to a 21th century battleground for ideas about ancient access and use rights of community members facing rights of a commercial forest owner and the local consequences of national legislation.
Alliances for Religions and Conservations (ARC) “Faith Engagement in Climate Smart Agriculture and Sustainable Land Management in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda
This is a desk appraisal of the Alliances for Religions and Conservations (ARC) done for the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (Norad) by the Department of International Environment and Development Studies, Noragric, at the Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU).
Does Ethiopia's productive safety net program improve child nutrition?
We study the link between Ethiopia’s Productive Safety Net Program (PSNP) and short-run nutrition outcomes among children age 5 years and younger. We use 2006 and 2010 survey data from Northern Ethiopia to estimate parameters of an exogenous switching regression. This allows us to measure the differential impacts of household characteristics on weight-for-height Z-score of children in member and non-member households in PSNP. We find that the magnitude and significance of household covariates differ in samples of children from PSNP and non-PSNP households.
Land valuation and perceptions of land sales prohibition in Ethiopia
This study investigates attitudes towards legalizing land sales and Willingness to Accept (WTA) sales prices and compensation prices for land among smallholder households in four different areas in the Oromia and SNNP Regions in the southern highlands of Ethiopia. Household panel data from 2007 and 2012 are used. The large majority of the sample prefers land sales to remain illegal, and the resistance to legalizing land sales increased from 2007 to 2012. In the same period, perceived median real land values increased sharply but also exhibit substantial local variation.
Agricultural household models for Malawi : household heterogeneity, market characteristics, agricultural productivity, input subsidies, and price shocks : a baseline report
This report documents agricultural household models developed for agricultural policy analyses related to the assessment of impacts of agricultural input subsidies and maize technology choices in Malawi. The models have been calibrated to a typology of households in Central and Southern Regions of Malawi based on household survey data collected for the period 2005-2010. Households are assumed to be drudgery averse and rational given their preferences and the resource constraints and imperfect markets they face.